Looking for a PCOS diet plan? This comprehensive guide provides valuable information and practical tips to successfully navigate a PCOS-friendly diet, supporting your journey towards wellness. Whether you need meal plans, recipes, or nutritional advice, this guide has got you covered.
In the realm of women’s health, PCOS, or Polycystic Ovary Syndrome, is a complex condition that affects many aspects of a woman’s body, including hormone levels, menstrual cycles, and fertility. For those diagnosed with PCOS, managing symptoms can often prove challenging. However, a well-structured diet plan can play a vital role in alleviating these symptoms and promoting overall wellness. In this comprehensive guide, you will find valuable information and practical tips to navigate a PCOS diet plan successfully, empowering you to take control of your health and embrace a fulfilling lifestyle. Whether you’re looking for specific meal plans, recipe inspiration, or tailored nutritional advice, this guide will serve as your ultimate resource to support your journey towards wellness.

Understanding PCOS
What is PCOS?
Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) is a hormonal disorder that affects women of reproductive age. It is characterized by the presence of cysts on the ovaries, hormonal imbalances, and various symptoms that can have a significant impact on a woman’s overall well-being.
Causes of PCOS
The exact cause of PCOS is still unknown, but it is believed to be influenced by a combination of genetic and environmental factors. Insulin resistance, hormonal imbalances, and inflammation are thought to play a role in the development of PCOS.
Symptoms of PCOS
PCOS presents a range of symptoms that can vary from woman to woman. Some common symptoms include irregular or absent menstrual periods, excessive hair growth (hirsutism), acne, weight gain, and difficulty in conceiving. These symptoms can significantly impact quality of life and require appropriate management.
Effects of PCOS on Diet
PCOS can have a profound impact on diet and nutrition. Insulin resistance, a common feature of PCOS, can lead to weight gain and difficulties in managing blood sugar levels. Additionally, hormonal imbalances can affect appetite regulation and increase cravings for unhealthy foods. Therefore, adopting a PCOS-friendly diet plan is crucial for managing the condition effectively and improving overall health.
Creating a PCOS Diet Plan
Consulting a Healthcare Professional
Before embarking on any dietary changes, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional, such as a registered dietitian or endocrinologist, who specializes in PCOS. They can provide personalized recommendations and help develop a tailored diet plan that suits your individual needs and goals.
Determining Individual Goals
Establishing clear goals is an essential part of creating a PCOS diet plan. Whether the aim is to manage weight, improve insulin sensitivity, regulate menstrual cycles, or enhance fertility, clearly defining these goals will help guide the dietary choices and strategies implemented.
Choosing the Right Foods
The foundation of a PCOS diet plan should be built on whole, nutrient-dense foods. Focus on incorporating a variety of fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, whole grains, and healthy fats into your meals. These foods provide essential vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants that support overall health and can help manage PCOS symptoms.
Portion Control
Maintaining portion control is crucial when managing PCOS. Monitoring the amount of food consumed can help regulate calorie intake and support weight management goals. Using measuring cups, food scales, or visual cues can assist in achieving appropriate portion sizes.
Meal Planning and Prep
Meal planning and preparation are key strategies for maintaining a consistent and nutritious diet. Plan your meals and snacks ahead of time, considering a balanced combination of macronutrients—protein, carbohydrates, and fats. Prepared meals and snacks can help prevent impulsive food choices and ensure a well-rounded diet.
Hydration Importance
Adequate hydration is vital for overall health and plays a significant role in managing PCOS symptoms. Aim to consume at least 8 cups (64 ounces) of water per day, or more if physically active. Additionally, incorporating hydrating foods such as fruits, vegetables, and herbal teas can contribute to overall hydration levels.
Avoiding Trigger Foods
Certain foods and ingredients may exacerbate PCOS symptoms and should be avoided or limited in a PCOS diet plan. These include processed and refined foods, sugary foods and beverages, highly caffeinated drinks, trans fats, excessive salt intake, alcohol, soy products, and foods with added hormones.
Supplements for PCOS
In some cases, healthcare professionals may recommend specific supplements to complement the PCOS diet plan. Common PCOS supplements include inositol, omega-3 fatty acids, vitamin D, and chromium. It’s important to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new supplements to ensure they are safe and suitable for your individual needs.
Importance of Exercise
In addition to dietary changes, regular physical activity is integral in managing PCOS. Exercise can help improve insulin sensitivity, support weight management, regulate hormones, reduce stress, and promote overall well-being. Choose exercises that you enjoy and can sustain in the long term, such as aerobic activities, strength training, or yoga.
Tracking Progress
Monitoring and tracking progress is essential in determining the effectiveness of the PCOS diet plan and making necessary adjustments. Keep a food diary to record meals, snacks, and portion sizes, as well as any symptoms or changes experienced. Regularly weigh yourself and track any changes in weight, hormonal balance, and overall well-being. Be sure to schedule regular check-ups with your healthcare provider to discuss progress and make any necessary adjustments to the diet and lifestyle plan.
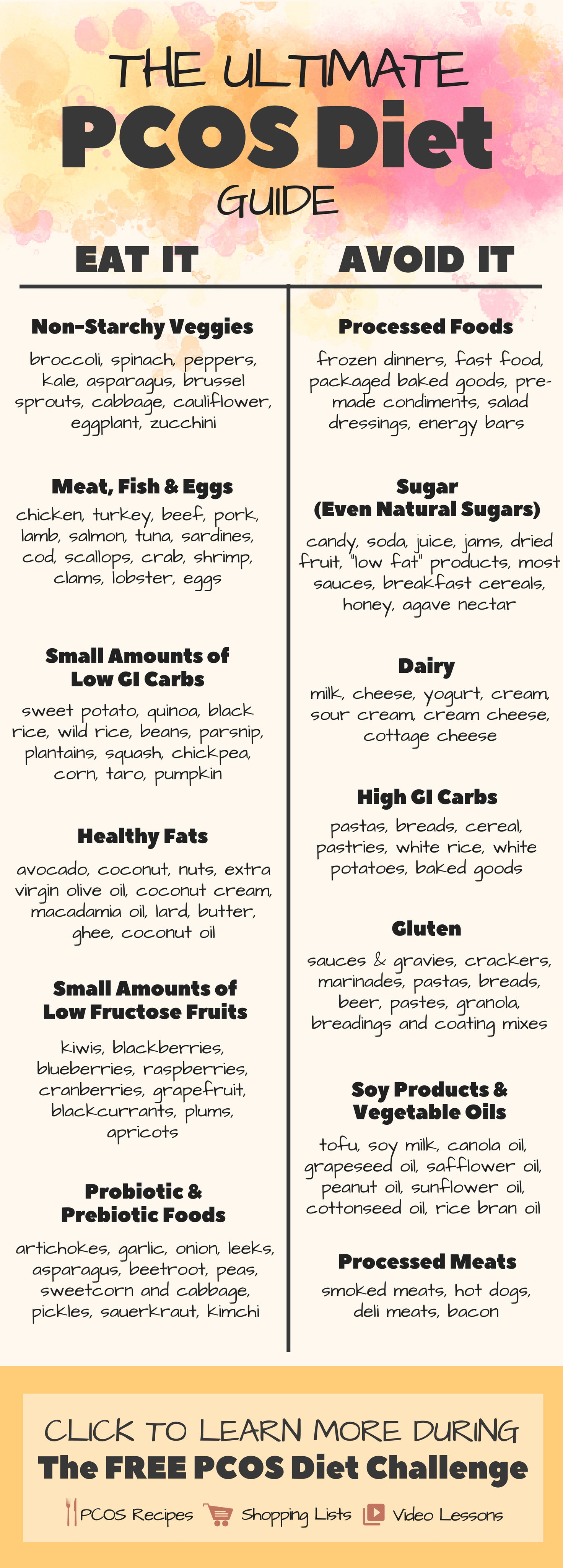
PCOS Diet: What to Eat
Foods Rich in Fiber
Including high-fiber foods in a PCOS diet plan can aid in managing weight, regulating blood sugar levels, and promoting gut health. Opt for whole grains, legumes, fruits, and vegetables to increase fiber intake.
Lean Protein Sources
Incorporating lean sources of protein into your meals helps in maintaining satiety, supporting muscle growth, and stabilizing blood sugar levels. Choose options such as skinless poultry, fish, tofu, beans, and lentils.
Low-Glycemic Index Carbohydrates
Selecting low-glycemic index (GI) carbohydrates can assist in managing blood sugar levels and reducing insulin resistance. Foods such as quinoa, sweet potatoes, whole-wheat pasta, and berries have a lower impact on blood sugar compared to high GI carbohydrates.
Healthy Fats
Including healthy fats in a PCOS diet plan is crucial for hormone production, satiety, and nutrient absorption. Opt for sources like avocados, nuts, seeds, olive oil, and fatty fish like salmon or sardines.
Fruits and Vegetables
Fruits and vegetables are packed with essential nutrients, antioxidants, and fiber. Aim for a variety of colorful options to obtain a wide range of vitamins and minerals. Incorporating them into salads, smoothies, or as snacks can help meet daily intake recommendations.
Dairy and Alternatives
Dairy products can be part of a PCOS diet plan, but it is important to choose low-fat options. If lactose intolerant or prefer alternatives, consider unsweetened plant-based milk alternatives like almond or soy milk.
Mindful Eating
Practicing mindful eating techniques involves being present in the moment and paying attention to hunger cues, fullness levels, and taste sensations. This approach can help prevent overeating, enhance satisfaction from meals, and promote a healthier relationship with food.
Including Herbal Teas
Herbal teas can provide various health benefits and contribute to hydration goals. Chamomile, spearmint, and peppermint teas are known for their calming effects and potential positive impacts on hormone regulation.
PCOS Diet: What to Avoid
Processed and Refined Foods
Processed and refined foods, such as white bread, sugary cereals, and packaged snacks, should be minimized or eliminated from a PCOS diet plan. These foods are often high in added sugars, unhealthy fats, and lack essential nutrients.
Sugary Foods and Beverages
Sugary foods and beverages, including soda, juice, pastries, and candies, can spike blood sugar levels and lead to weight gain. Eliminating or reducing these items is crucial for managing PCOS symptoms and maintaining overall health.
Highly Caffeinated Drinks
Highly caffeinated drinks, such as energy drinks or excessive coffee consumption, can disrupt hormone balance, affect sleep quality, and contribute to anxiety or mood swings. It is advisable to limit or avoid these beverages.
Trans Fats
Trans fats are unhealthy fats commonly found in processed foods, fried foods, and commercially baked goods. They can increase inflammation and worsen insulin resistance, leading to metabolic complications. Avoid products that list hydrogenated or partially hydrogenated oils in their ingredients.
Excessive Salt Intake
Excessive salt intake can contribute to water retention and increase blood pressure. Reducing salt intake by avoiding processed foods and opting for fresh, whole foods can help manage PCOS-related bloating and support heart health.
Alcohol Consumption
Alcohol intake should be limited or avoided, as it can negatively impact hormonal balance, worsen insulin resistance, and interfere with nutrient absorption. Additionally, alcoholic beverages are often high in empty calories and can contribute to weight gain.
Soy Products
Soy products contain phytoestrogens, which can mimic estrogen in the body. While some women with PCOS may tolerate soy, others may experience adverse effects. Consult with a healthcare professional to determine if soy products are suitable for your diet plan.
Foods with Added Hormones
Foods with added hormones, such as conventional dairy and meat products, can disrupt hormone balance and worsen PCOS symptoms. Opt for organic and hormone-free options whenever possible.

Meal Planning Tips
Balancing Macronutrients
A balanced PCOS diet plan should include a combination of macronutrients—protein, carbohydrates, and fats. Aim to distribute these macronutrients evenly throughout the day to support energy levels, stabilize blood sugar, and promote satiety.
Regular Meal Times
Establishing regular meal times is important for managing PCOS symptoms. Consistent meal times can help regulate appetite, prevent excessive hunger, and support blood sugar control. Aim to eat every 3 to 4 hours, spacing meals and snacks evenly throughout the day.
Importance of Breakfast
Breakfast is often considered the most important meal of the day. Including a balanced breakfast in a PCOS diet plan can jumpstart metabolism, stabilize blood sugar, and provide sustainable energy for the day ahead. Incorporate protein, fiber, and healthy fats into your breakfast options.
Healthy Snack Ideas
Planning and preparing healthy snacks can help prevent impulsive food choices and overeating. Opt for nutrient-dense snacks such as raw nuts, Greek yogurt, sliced fruits and vegetables, or homemade energy bars. These options provide satisfaction and support satiety between meals.
Cooking Methods
Choosing healthy cooking methods is important to ensure nutrient preservation and minimize the use of unhealthy fats. Opt for methods such as baking, grilling, steaming, or sautéing with minimal oil.
Mindful Eating Practices
Mindful eating involves paying attention to hunger and fullness cues, eating slowly, and savoring the taste and texture of each bite. This approach can promote better digestion, prevent overeating, and foster a positive relationship with food.
Eating Out Strategies
Eating out can pose challenges to a PCOS diet plan, but with some strategies, it can still be manageable. Researching menu options ahead of time, choosing restaurants with healthier choices, opting for grilled or baked dishes, and asking for modifications can help make healthier choices while dining out.
Ingredient Substitutions
Modifying recipes and substituting ingredients can allow for healthier alternatives in a PCOS diet plan. For example, replacing refined grains with whole grains, using low-fat dairy or plant-based alternatives, or swapping unhealthy fats for healthy fats can enhance the nutritional value of meals.
Dining with Non-PCOS Individuals
Navigating meals with non-PCOS individuals can present unique challenges. Open communication, educating others about your dietary needs, and finding common ground in menu choices can help create a supportive and inclusive environment.
Meal Planning Apps and Tools
Utilizing meal planning apps or tools can simplify the process of creating a PCOS diet plan. These resources offer recipe ideas, grocery lists, and meal tracking features, making it easier to stay organized and maintain dietary goals.
Portion Control and Management
Understanding Portion Sizes
Understanding appropriate portion sizes is crucial for managing PCOS and promoting healthy weight management. It is important to learn to recognize recommended serving sizes for different food groups and adjust accordingly.
Using Portion Control Tools
Portion control tools can be helpful in maintaining appropriate portion sizes. Measuring cups, kitchen scales, or visual cues such as using the palm of your hand or a deck of cards can serve as reference points to achieve balanced portions.
Meal Frequency and Size
Determining appropriate meal frequency and size is individualized and may vary based on personal preferences and goals. Some individuals may prefer three larger meals, while others may prefer smaller, more frequent meals. Listen to your body’s hunger and fullness signals to determine what works best for you.
Plate Composition
The composition of each meal is important for proper balance and nutrient intake. Aim to fill half of your plate with non-starchy vegetables, one-quarter with lean protein, and one-quarter with whole grains or starchy vegetables. Additionally, include a serving of healthy fats or dairy alternatives.
Mindful Eating Techniques
Practicing mindful eating techniques, such as eating slowly, chewing thoroughly, and savoring each bite, can help promote portion control and prevent overeating. Focus on the sensory experience of eating and listen to your body’s natural cues of hunger and satiety.

Importance of Hydration
Benefits of Proper Hydration
Proper hydration is essential for overall health and well-being, including managing PCOS symptoms. It aids in digestion, nutrient absorption, regulating body temperature, maintaining healthy skin, and supporting hormonal balance.
Determining Water Intake
Determining an adequate water intake can vary based on individual needs, activity levels, and climate. Generally, aiming to consume at least 8 cups (64 ounces) of water per day is a good starting point, but some individuals may require more.
Hydrating Foods and Drinks
In addition to plain water, consuming hydrating foods and drinks can contribute to overall hydration. Foods with high water content, such as cucumbers, watermelon, and spinach, as well as herbal teas or infused water, can support hydration goals.
Creating a Hydration Routine
Creating a hydration routine can help ensure adequate fluid intake throughout the day. Establishing habits such as drinking a glass of water upon waking, carrying a water bottle for easy access, and setting reminders can support consistent hydration.
Exercise and PCOS
Benefits of Exercise for PCOS
Exercise plays a crucial role in managing PCOS symptoms and improving overall health. Regular physical activity can help regulate hormones, improve insulin sensitivity, support weight management, reduce stress, and boost mood.
Choosing the Right Exercise
Choosing the right type of exercise is essential for individuals with PCOS. Opt for activities that you enjoy and can sustain in the long term. Aerobic exercises such as walking, jogging, swimming, cycling, or dancing, as well as strength training exercises, can be beneficial for PCOS management.
Creating an Exercise Routine
Creating a consistent exercise routine is important for establishing long-term habits and reaping the benefits of regular physical activity. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity aerobic exercise per week, along with two or more days of strength training.
Combining Cardio and Strength Training
Incorporating both cardio and strength training exercises into a PCOS exercise routine provides a comprehensive approach to managing symptoms. Cardio exercises improve cardiovascular health and aid in weight management, while strength training helps build muscle, improve metabolism, and enhance body composition.
Tracking Fitness Progress
Tracking fitness progress can provide motivation and help evaluate the effectiveness of the exercise routine. Keep a record of workout duration, intensity, and type, as well as changes in endurance, strength, or body measurements over time. This information can guide future workouts and highlight achievements.
Exercising with PCOS Challenges
Exercising with PCOS may present unique challenges such as fatigue, hormonal imbalances, or joint pain. It is important to listen to your body, modify exercises if needed, and seek guidance from healthcare professionals or exercise specialists who understand the specific needs of individuals with PCOS.
Incorporating Physical Activity in Daily Life
In addition to structured exercise sessions, finding ways to incorporate physical activity into daily life can contribute to overall movement and energy expenditure. Simple habits like taking the stairs instead of the elevator, walking or cycling instead of driving short distances, or engaging in active hobbies can support an active lifestyle.

Supplements for PCOS
Consultation with a Doctor
Before starting any supplements, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional who can evaluate your individual needs and determine if supplementation is necessary. They can assess potential interactions with medications and provide guidance on proper dosage and timing.
Common PCOS Supplements
Certain supplements may be beneficial for managing PCOS symptoms and supporting overall health. Some common supplements recommended for PCOS include inositol, omega-3 fatty acids, vitamin D, and chromium. However, it is important to remember that individual needs may vary, and supplementation should be personalized under professional guidance.
Effectiveness and Safety
The effectiveness and safety of PCOS supplements vary depending on the individual and the specific supplement. While some studies suggest potential benefits, it is important to approach supplementation cautiously and ensure high-quality products from reputable sources are chosen.
Finding High-Quality Supplements
When considering supplements, it is crucial to choose high-quality products from reputable brands. Look for third-party testing, certification seals, and verified reviews to ensure the supplements meet safety and quality standards.
Proper Dosage and Timing
Proper dosage and timing are key factors in maximizing the benefits of PCOS supplements while minimizing potential side effects. Always follow the recommended dosage instructions provided by healthcare professionals or the supplement manufacturer.
Tracking Progress and Adjustments
Using a Food Diary
Keeping a food diary is an effective way to track dietary habits and identify areas for improvement. Write down meals, snacks, portion sizes, and accompanying symptoms or changes in PCOS symptoms. This record can provide insight into the relationship between diet and well-being.
Monitoring Weight Changes
Monitoring weight changes is important, especially for individuals with weight-related PCOS symptoms. Regularly weigh yourself using consistent scales and techniques, and track any changes over time. However, it is essential to remember that weight is just one aspect of overall health, and focusing solely on the number on the scale may not reflect other positive changes in the body.
Tracking Hormonal Balance
In addition to weight, tracking hormonal balance is crucial for individuals with PCOS. Monitoring menstrual cycles, tracking changes in hirsutism or acne, and assessing hormone levels through blood tests can provide valuable information to evaluate the effectiveness of the PCOS diet plan and make necessary adjustments.
Regular Doctor Check-ups
Regular check-ups with a trusted healthcare provider are essential for managing PCOS. They can assess progress, monitor hormone levels, provide guidance, and make any necessary adjustments to the PCOS diet plan or supplementation regimen. Open communication with healthcare professionals is key to ensure the best possible management of PCOS.
Identifying and Adapting to Individual Needs
Every individual with PCOS is unique, and different approaches may be necessary for effective symptom management. Identifying individual needs, considering genetic factors, addressing underlying health conditions, and working closely with healthcare professionals can ensure a personalized approach to managing PCOS through diet and lifestyle changes.
In conclusion, a comprehensive PCOS diet plan involves understanding the condition, seeking professional guidance, and making informed choices about the foods consumed. Prioritizing nutrient-dense whole foods, practicing portion control, staying adequately hydrated, engaging in regular exercise, and tracking progress can all contribute to managing PCOS symptoms and improving overall health. Remember, individual needs may vary, so consult with healthcare professionals to develop a tailored plan that suits your specific goals and requirements.
