Discover the truth behind the claim that diarrhea can aid in weight loss. Explore the science, risks, and implications of this unconventional method.
n the quest for weight loss, individuals are often willing to explore unconventional methods, even to the extent of questioning whether diarrhea may contribute to shedding unwanted pounds. This peculiar yet intriguing notion has garnered attention, prompting individuals to delve into the topic further. This article will examine the potential correlation between diarrhea and weight loss, shedding light on the physiological factors at play and addressing the validity of this assertion. By exploring scientific research and medical insights, a clearer understanding will emerge regarding the veracity of this curious theory and its implications for weight management.
Can Diarrhea Help You Lose Weight?
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/losing-weight-with-ibs-1945012-01-987b235a57b240e4903560c79416288b.png)
Understanding Diarrhea
Diarrhea is a condition characterized by loose or watery stools, often accompanied by increased frequency and urgency. It is a common condition that can be caused by various factors such as infections, foodborne illnesses, digestive disorders, medications, and stress or anxiety. The symptoms of diarrhea include abdominal cramping, bloating, and the passing of loose stools multiple times in a day.
Diarrhea and Weight Loss
The relationship between diarrhea and weight loss is often a topic of interest, as some people wonder if experiencing diarrhea can lead to shedding pounds. While it is true that diarrhea can cause temporary weight loss, it is important to understand the underlying causes and potential risks associated with relying on diarrhea as a weight loss method.
The Link between Diarrhea and Weight Loss
Diarrhea can lead to weight loss through various mechanisms. Firstly, it increases the body’s caloric expenditure as the intestines work harder to eliminate waste. This rise in metabolic activity may result in the burning of additional calories. Secondly, diarrhea can lead to water loss, which can cause a temporary decrease in body weight. Additionally, diarrhea can impact the absorption of essential nutrients, leading to deficiencies and potential loss of muscle mass. Lastly, diarrhea can affect appetite and hunger cues, resulting in reduced food intake.
Causes of Diarrhea
Diarrhea can be caused by a wide range of factors, including infections such as viral, bacterial, or parasitic infections. Foodborne illnesses, often contracted through contaminated food or water, can also trigger diarrhea. Digestive disorders such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), celiac disease, and lactose intolerance can contribute to chronic diarrhea. Certain medications, such as antibiotics and laxatives, can also induce diarrhea as a side effect. Finally, stress and anxiety can disrupt the normal functioning of the digestive system and lead to diarrhea.
The Effect of Diarrhea on the Body
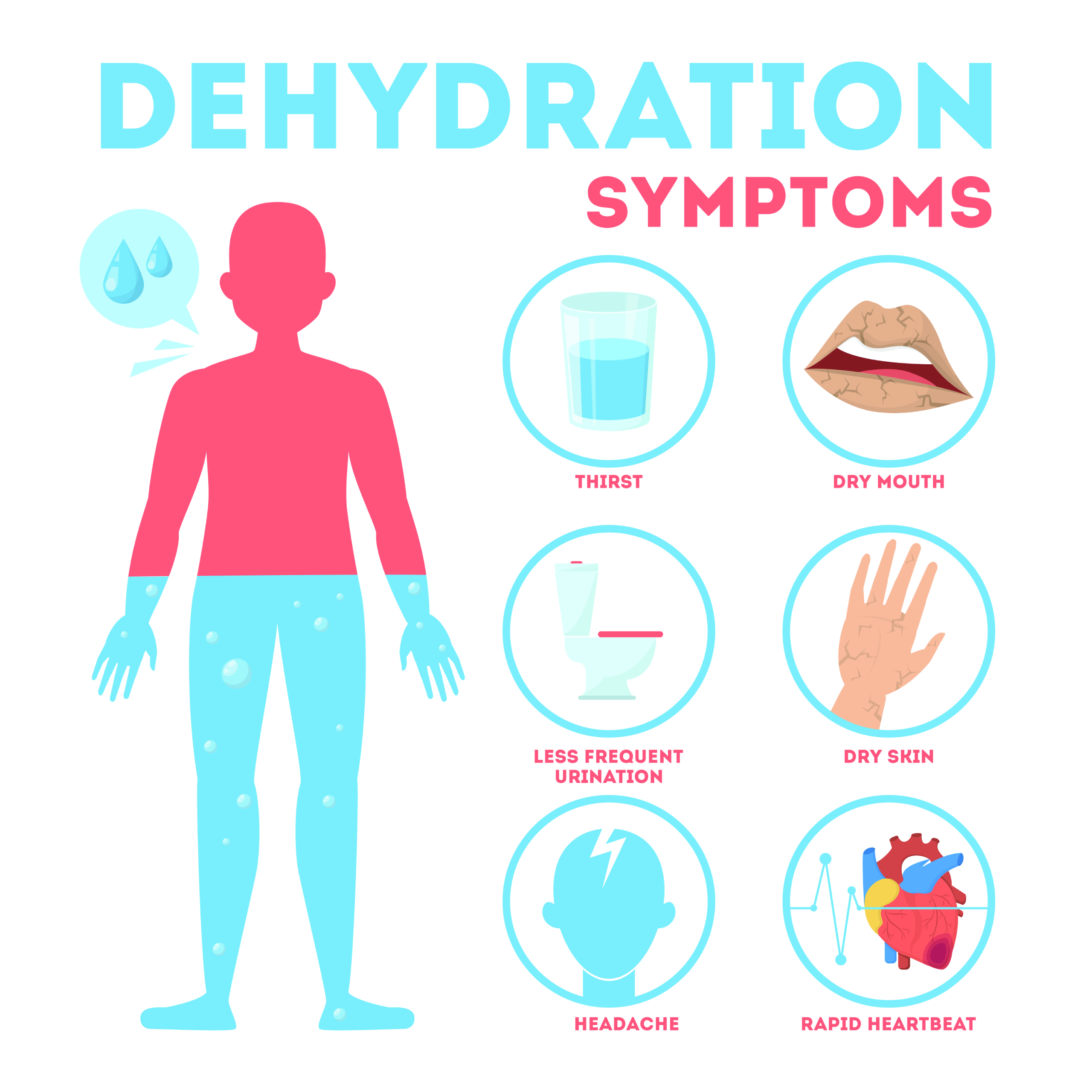
Diarrhea can have several effects on the body. One of the primary concerns is fluid loss and dehydration, as diarrhea can cause excessive water elimination from the body. This can result in symptoms such as increased thirst, dry mouth, decreased urine output, and dizziness. Electrolyte imbalances can also occur due to the loss of minerals like sodium, potassium, and magnesium through diarrhea. Inadequate hydration and electrolyte imbalances can lead to weakness, muscle cramps, and even heart rhythm abnormalities. Moreover, persistent diarrhea can deplete the body’s energy reserves and contribute to fatigue and weakness. Lastly, diarrhea can disrupt normal bowel movements, leading to irregularity and potential long-term digestive issues.
Dehydration and Electrolyte Imbalance
Dehydration is a significant concern when experiencing diarrhea. Signs of dehydration include increased thirst, dry mouth, decreased urine output, dark-colored urine, and lightheadedness. Electrolytes, such as sodium, potassium, and magnesium, play essential roles in the body’s functioning. Diarrhea can disrupt electrolyte balance, leading to deficiencies or excesses of these vital minerals. Electrolyte imbalances can result in muscle cramps, weakness, irregular heartbeats, and in severe cases, life-threatening complications like seizures.
Impact on Nutrient Absorption
Diarrhea can impair the body’s ability to absorb nutrients properly. Malabsorption, characterized by inadequate absorption of nutrients from the gastrointestinal tract, can occur due to the rapid transit of food through the intestines during diarrhea. This can lead to deficiencies in vitamins and minerals, potentially causing a range of symptoms and health issues. Without proper nutrient absorption, the body may struggle to maintain optimal function and overall health. Impaired digestion and absorption can also lead to digestive discomforts such as bloating and increased gas production.
Digestive System Health
Maintaining a healthy digestive system is crucial for overall well-being. The digestive system is responsible for breaking down food, absorbing nutrients, and eliminating waste. Diarrhea can disrupt this delicate balance and compromise digestive system health. The gut microbiota, a complex community of microorganisms residing in the intestines, plays a crucial role in digestion and nutrient absorption. Diarrhea can disrupt the balance of this microbiota, impacting overall digestive function. Taking steps to support a healthy digestive system, such as consuming a balanced diet, managing stress, and promoting a diverse gut microbiome, can help prevent diarrhea and support long-term health.
Temporary Weight Loss
While diarrhea may lead to temporary weight loss, it is important to recognize that this weight loss is not sustainable or healthy. The weight lost during diarrhea mostly includes water weight and is not indicative of fat loss. As soon as normal hydration and eating patterns are resumed, the weight lost through diarrhea is likely to be regained. Relying on diarrhea as a weight loss method can lead to nutrient deficiencies, electrolyte imbalances, and potential long-term health complications.
Potential Dangers of Using Diarrhea as a Weight Loss Method
Using diarrhea as a deliberate weight loss method is not only ineffective but also potentially dangerous. It can lead to dehydration, electrolyte imbalances, and malnutrition. Prolonged diarrhea can also harm the digestive system by disrupting the gut microbiota and impairing its ability to absorb nutrients properly. Additionally, relying on diarrhea for weight loss neglects the importance of sustainable and healthy lifestyle changes, such as proper nutrition, regular physical activity, and stress management.
Diarrhea and Weight Loss: Is it Sustainable?
In conclusion, while diarrhea may lead to temporary weight loss, it is not a sustainable or healthy method for achieving long-term weight management goals. Diarrhea can cause dehydration, electrolyte imbalances, and nutrient deficiencies, which can have detrimental effects on overall health. Instead of resorting to potentially harmful methods, individuals should prioritize adopting a balanced and nutritious diet, engaging in regular physical activity, and seeking guidance from healthcare professionals for safe and effective weight loss strategies. Sustainable weight loss is best achieved through a holistic approach that promotes overall well-being rather than relying on temporary and potentially dangerous methods such as inducing diarrhea.

